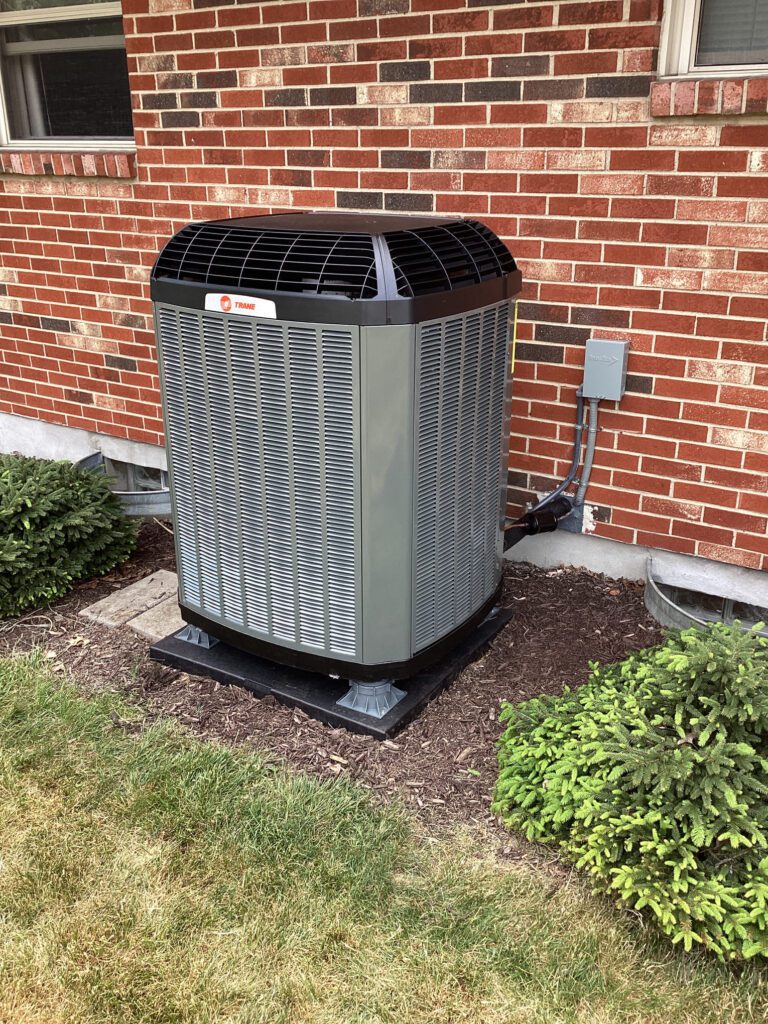
Heat pumps have revolutionized the world of heating and cooling by offering energy-efficient solutions for maintaining comfortable indoor environments. To truly appreciate the efficiency and functionality of heat pumps, it’s essential to delve into their intricate components that work harmoniously to regulate temperatures effectively. Let’s explore the core components of heat pumps, their functions, and the evolving landscape of heat pump technology.
Definition and Function of a Heat Pump
At its core, a heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one location to another. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat, heat pumps utilize the principles of thermodynamics to extract heat from the surrounding environment and move it indoors during colder months. In the warmer months, the process is reversed to expel indoor heat, keeping the space cool.
Importance of Understanding the Components of a Heat Pump
Understanding the various components of a heat pump is vital for homeowners and technicians. It empowers homeowners to diagnose minor issues and appreciate the importance of regular maintenance. For technicians, a deep understanding of these components enables them to perform effective repairs and installations, ensuring the optimal performance of the system.
How Heat Pumps Differ from Traditional Heating Systems
Traditional heating systems, such as furnaces or electric heaters, generate heat through combustion or electrical resistance. This method consumes more energy compared to heat pumps, which rely on the movement of heat rather than the direct creation of it. Heat pumps are more energy-efficient as they transfer existing heat from the environment to maintain indoor comfort.
Core Components of a Heat Pump
Compressor: The Heart of the Heat Pump
The compressor serves as the beating heart of a heat pump system. Its primary function is to pressurize the refrigerant gas, elevating both its temperature and pressure significantly. This process transforms the refrigerant into a high-energy, high-temperature gas. The high-pressure gas is then directed towards the condensing coil for further heat exchange.
Evaporator Coil: Extracting Heat from the Ambient Air
The evaporator coil plays a crucial role in the heat pump’s ability to extract heat from the surroundings, be it from the air or the ground, depending on the type of heat pump. As the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant flows through the evaporator coil, it undergoes a phase change, turning into a low-energy gas. This phase transition is accompanied by a significant drop in temperature.
By absorbing heat from the surrounding environment, the evaporator coil facilitates the cooling or heating process within the heat pump system.
Condensing Coil: Releasing Heat into Your Home
The condensing coil receives the high-energy, high-temperature gas discharged from the compressor. Its primary function is to aid in the release of heat into the indoor environment.
As the hot gas circulates through the condensing coil, it gradually loses heat energy, causing it to condense back into a liquid state. This condensation process releases a considerable amount of heat, which is distributed throughout the home, providing warmth during colder months.
Air Handler: System’s Fan Component to Circulate Air
The air handler contains a fan that is responsible for circulating air over the evaporator and condensing coils. This fan plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency of the heat transfer processes.
By moving air over these coils, the air handler helps facilitate the exchange of heat between the refrigerant and the indoor air, ensuring that conditioned air is evenly distributed throughout the living space. This distribution is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature.
Reversing Valve: Essential for the Heat Pump’s Dual Function
The reversing valve is a critical component that enables the heat pump to switch between its heating and cooling modes. It accomplishes this by changing the direction of the refrigerant flow within the system.
When in heating mode, the reversing valve directs the refrigerant to release heat into the indoor environment. In cooling mode, it reverses the flow, allowing the heat pump to absorb heat from indoors and release it outside.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve: Regulating the Flow of Refrigerant
The thermostatic expansion valve is responsible for controlling the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. It accomplishes this by regulating the refrigerant’s expansion and ensuring it enters the coil at the right rate. This precise control of refrigerant flow helps maintain the proper balance between temperature and pressure, which is crucial for efficient heat exchange within the system.
Defrost Control: Keeping the System Running in Icy Conditions
In colder climates, frost and ice can accumulate on the outdoor unit’s coil during heating mode. This accumulation can impede the system’s efficiency. The defrost control feature is designed to tackle this issue by initiating periodic defrost cycles. These cycles temporarily reverse the heat pump’s operation, melting the frost and ice on the outdoor coil to maintain optimal performance even in icy conditions.
Maintenance of Heat Pump Parts and Efficient Operation
The Importance of Regular Inspection and Tuning-up
To ensure the longevity and efficiency of a heat pump, regular inspections and tune-ups are crucial. This involves checking refrigerant levels, cleaning coils, replacing filters, and verifying the performance of various components such as the heat pump capacitor. Routine maintenance not only prolongs the system’s lifespan but also ensures it operates at peak efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Heat Pump Parts
Understanding common issues that can arise in heat pump components is essential for homeowners. Low refrigerant levels, dirty coils, electrical problems, and airflow restrictions can all impact the system’s performance. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly can prevent larger problems down the line.
Replacements and Upgrades: Making Your Heat Pump More Efficient
As heat pump technology advances, older components may become outdated and less efficient. Upgrading certain parts or even the entire system can lead to improved energy efficiency, enhanced performance, and increased cost savings over time. It’s best to work with trusted HVAC professionals who can assess the current state of your heat pump and recommend improvements.
Outdoor Parts of a Heat Pump
Now, let’s review the outdoor components of a heat pump:
- Outdoor Unit: The outdoor unit houses critical components such as the compressor, condensing coil, and reversing valve. It is exposed to various weather conditions, making regular maintenance and protection essential for optimal performance.
- Refrigerant: Refrigerant is the medium that facilitates the heat transfer process in a heat pump. It absorbs heat when evaporating and releases heat when condensing, playing a central role in the system’s operation.
Different Types of Heat Pumps and Their Unique Parts
So what kinds of heat pumps are available to homeowners? Here is a breakdown:
- Air Source Heat Pumps: Air heat pumps extract heat from the outdoor air and transfer it indoors. They are equipped with the same core components but vary in efficiency based on factors such as climate and installation quality.
- Ground Source Heat Pumps (Geothermal): Ground source heat pumps, or geothermal heat pumps, extract heat from the ground through a loop system. They offer exceptional efficiency but require a more complex installation process due to the ground loop.
- Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps: Ductless mini-split heat pumps consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units. They are a versatile solution for homes without existing ductwork and offer zone-specific climate control.
The Future of Home Heating: Advances in Heat Pump Technology
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into heat pumps allows for remote monitoring and control. Smart thermostats and connected systems enable users to optimize energy usage and comfort. In addition, heat pumps may continue to integrate environmentally friendly technology. Heat pumps can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar panels. This combination significantly reduces carbon emissions and contributes to a greener future.
Making the Most Out of Your Heat Pump
Understanding the various components of a heat pump provides valuable insights into how these systems work and the importance of regular maintenance. By recognizing the roles that components like the compressor, evaporator coil, and reversing valve play, homeowners and technicians can ensure the efficient operation of heat pumps and enjoy comfortable indoor environments year-round.
Look to Logan Services A/C, Heat & Plumbing for Your HVAC Needs
Whether you need help with your heat pump or another part of your HVAC system, Logan Services is here to help. As a family-owned and operated business, we always put our customers first. Logan’s trained technicians and installers go through intensive training to bring you quality HVAC workmanship. In addition, our team is committed to answering your questions and communicating clearly throughout the process. If you need to purchase a new heat pump or AC unit, our install managers have years of experience offering comprehensive support throughout the process.
We are proud to be part of the community offering outstanding support. Contact us today to get started.