Heat pumps have become increasingly popular for heating and cooling homes. They can reduce energy costs and provide efficient temperature control. However, one concern people have is whether heat pumps make disruptive noise. This article will look at the sources of noise in heat pumps, compare sound levels, and provide tips on reducing heat pump noise.
What Is a Heat Pump and How Does It Work?
A heat pump system is an HVAC system that transfers heat between your home and the outside air. It uses a refrigeration cycle with a compressor and a condenser to move heat. During heating mode, the outdoor unit absorbs heat from the outdoor air and pumps it indoors.
The process reverses in cooling mode, pulling heat from your home and emitting it outside.
Heat pumps provide an energy-efficient alternative to furnaces and air conditioners. As electricity gets cleaner, heat pumps will reduce emissions from home heating and cooling. Their popularity has been growing significantly in recent years.
What Causes Noise in a Heat Pump?

Though heat pumps don’t combust fuels like natural gas furnaces, they do have mechanical components that can generate common heat pump noises:
The Compressor
The compressor is the primary source of noise from a heat pump. It creates a consistent hum or whirring sound when operating as it rapidly compresses and circulates refrigerant through the system. Older single-speed compressors simply switched on and off at full speed. This on-off cycling creates a loud “start-up surge” each time the compressor starts. Newer inverter-driven variable speed compressors can smoothly adjust operating speeds and run much more quietly. They avoid the noisy on-off cycling of single-speed models. Carefully selecting an inverter heat pump and sizing the compressor properly for your home’s heating and cooling needs will minimize noise from the compressor. Installing the compressor section on vibration-absorbing mounts also helps reduce noise transmission from compressor operation.
Fans
Both the indoor air handler and outdoor condenser unit rely on fans to move air across heat exchangers and through ductwork. Fan noise arises from high-velocity turbulent airflow. Air moving at high speeds creates noticeable friction and turbulence noises. Larger, slower-moving fans can move the required airflow while keeping velocities lower to reduce turbulence and noise. High-quality, dynamically balanced fan blades and ball bearings also help reduce fan noise and vibration. Carefully selecting low-noise fans, using fan speed controllers, and isolating fans with insulated mounts reduce their sound levels. Strategically placing any bends in ductwork farther away from the air handler fan also lowers turbulence and noise. Designing your ductwork for the smoothest, least turbulent airflow possible prevents airflow noise from being amplified as it circulates through the duct system.
Defrost Cycle
Heat pumps periodically go into defrost mode to melt frost accumulating on the outdoor coils in cold weather. When a unit defrosts, the compressor may run at higher speeds to provide hot refrigerant gas that clears ice from the coils. The outdoor fan may also temporarily reverse flow to assist with defrosting. Both the high compressor speed and altered outdoor fan operation during defrost cycles will increase noise levels temporarily before returning to normal quiet operation.
Airflow Noise
In addition to the fan itself, noise results from air rushing through ducts, vents, and other components of the HVAC system. High airflow velocities create turbulence as the air encounters obstacles and changes in direction. This turbulence leads to pressure fluctuations that transmit through duct walls and other system components as audible noise. Multiple strategies can help reduce airflow noise. Properly sizing ductwork for the design airflow helps maintain velocities in the optimal range. Smooth ductwork fabrication with large radius gradual bends instead of sharp elbows minimizes turbulence. Lining duct interiors with sound-attenuating materials can absorb noise before it radiates outward. Well-insulated registers prevent noise breakout into living spaces while allowing efficient air distribution. Duct noise control is an important consideration in HVAC system design and installation to prevent nuisance noise issues. With careful attention to detail, airflow noise can be mitigated effectively.
How Loud Are Heat Pumps?
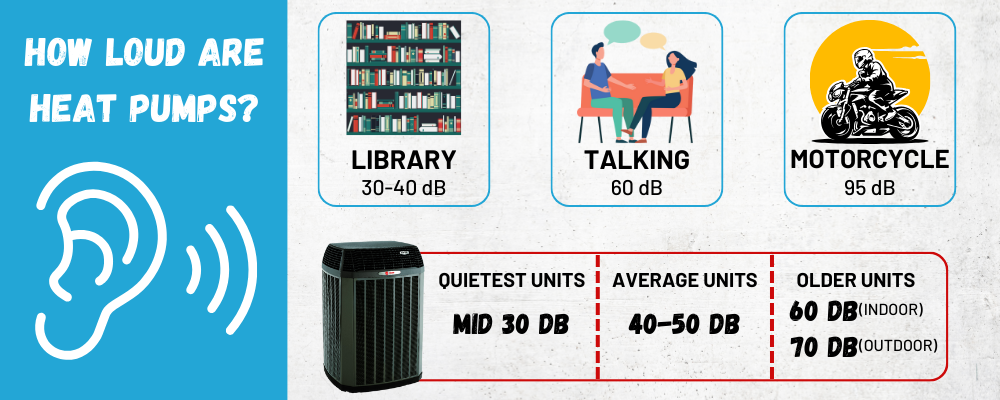
To measure sound level ratings, we use decibels (dB). The larger the decibel number, the louder the noise. Here are some comparisons:
- Library: 30-40 dB
- Refrigerator: 40-45 dB
- Conversation: 60 dB
- Vacuum: 70 dB
- Motorcycle: 95 dB
The quietest heat pumps operate in the mid 30 decibel range. Average units are in the 40-50 dB range. Older or improperly installed heat
pumps can reach up to 60 dB for indoor units and low 70s for outdoor units.
Proper installation is key to minimizing noise. Units should meet manufacturer specifications for clearances. Sound dampening techniques can further reduce noise.
How Does Heat Pump Noise Compare to Ambient Home Noise?
While 60 dB may seem loud for an indoor unit, this noise level blends with normal household activities. As examples:
- Dishwasher: 55-70 dB
- TV at normal volume: 60-65 dB
- Group conversation: 65-75 dB
With conversation and television providing consistent background noise around 60-65 dB in homes, a properly selected and installed heat pump won’t exceed normal sound levels.
Outdoor units are farther from living spaces. Placing them away from patios or decks keeps outdoor noise unobtrusive.
Tips for Reducing Heat Pump Noise
If you’re concerned about noise, here are ways to select and install a quieter heat pump:
Choose an Inverter Heat Pump
Inverter-driven compressors adjust speeds rather than simply cycling on and off. This removes the “start-up surge” that creates louder noise when starting. Less cycling also reduces wear.
Select a Model with a Quieter Outdoor Fan
Larger, slower-moving outdoor fans are quieter. Look for units with fans designed to reduce turbulence and noise. Ask manufacturers about sound ratings.
Use Sound Dampening Materials
Rubber grommets around mounts, acoustic liners in cabinets, and insulation around ductwork muffle vibrations and airflow noise.
Position the Outdoor Unit Thoughtfully
Place the outdoor unit as far as possible from windows and patios. Sound-dampening barriers also direct noise away from outdoor living areas.
Optimize Ductwork for Reduced Airflow Noise
Smooth ductwork, gradual bends, lined plenums, and insulated registers keep airflow quiet.
Conclusion: Heat Pumps Can Operate Quietly
Heat pumps do not have to generate excessive or disruptive noise when properly selected, designed, and installed. While all mechanical systems make some sound, today’s heat pump models can operate very quietly.
With inverter compressor technology, quieter fans, and sound-dampening techniques, indoor and outdoor noise can be comparable to existing background sound levels in a home. Heat pumps offer an energy-efficient way to heat and cool quietly and comfortably.
The Logan Difference:

At Logan Heating & Air Conditioning, we understand that noise from heat pumps can be a concern for homeowners. As a family-owned company that cares deeply about our customers and community, we take steps to ensure your heat pump operates as quietly and efficiently as possible. Our installers go through extensive training and follow detailed checklists on every job, allowing us to choose optimal locations and make any needed adjustments.
We walk through the entire setup process with customers, troubleshooting possible issues and explaining maintenance and warranty details before we leave. With experienced leadership guiding our qualified technicians, you can trust Logan Heating & Cooling to install your heat pump with care and expertise, minimizing noise while maximizing comfort and savings. As members of this community, we are committed to providing the high-quality service and support homeowners expect and deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
How loud are heat pumps inside the house?
With proper installation, most heat pumps produce less than 60 decibels of sound in normal operation. This is similar to noises like an everyday conversation at home. Models with inverter compressors run even more quietly.
Do heat pumps make high-pitched noises?
Some older heat pump compressors can produce high-pitched sounds. Modern inverter-driven compressors adjust operating speeds, avoiding high-pitched noise from cycling on and off.